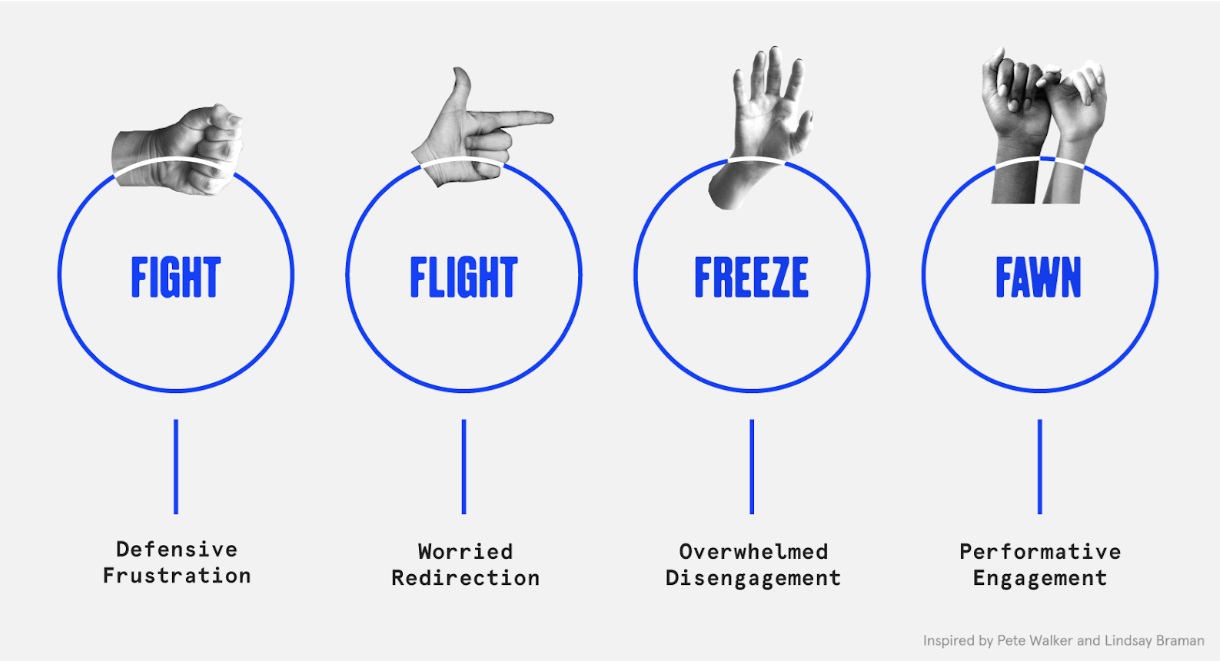
Fight/Flight, Tend/Befriend. Where are they now?
“I’m stressed” is a comment we hear in our day-to-day lives, we are told to avoid it but somehow the more we avoid it, the more it hovers over us. Despite advice to push through or ignore it, stress often seems to grow the more we avoid it. This article explores how our natural stress responses, originally designed to protect us, have become maladaptive, leading to confusion about our physical, mental, and emotional states when overwhelmed. How is it that what was once a physiological response meant to protect us has now become maladaptive, contributing to the very stress and confusion we seek to escape?
The fight-or-flight response is the body’s instinctive reaction to immediate threats, causing physical changes like increased heart rate and heightened alertness for quick action. In contrast, the tend-and-befriend response involves seeking social support and nurturing relationships, particularly in females, to cope with stress. Understanding these responses is crucial in today’s fast-paced world as it helps manage stress effectively, promotes better health by addressing both immediate and long-term stress, and enhances interpersonal relationships through supportive interactions.
The flight/fight response is an automatic reaction that prepares the body to either confront or flee from perceived threats. It is commonly triggered by stressful situations like emergencies, arguments, or other dangers. Physiologically, this response causes an increase in heart rate, elevated adrenaline levels, rapid breathing, muscle tension, and heightened senses to prepare for immediate action. Emotionally, individuals may experience anxiety, panic, fear, and agitation. If this response is activated frequently or for extended periods, it can lead to chronic stress, burnout, weakened immune function, cardiovascular problems, and other long-term health issues.
The tend/befriend response is a stress reaction characterized by seeking social support and nurturing relationships rather than engaging in confrontation or escape. This response is more common in situations where individuals face social or emotional stress, such as during relationship difficulties or when dealing with family challenges. Physiologically, the body reacts by releasing oxytocin, which promotes bonding and social connection. Emotionally, people often seek comfort, and support, and engage in caregiving behaviours. Long-term, this response can lead to improved social bonds and support networks, which are beneficial for emotional well-being. However, it can also pose challenges if it leads to excessive dependency on others or if individuals neglect their own needs in favour of others.
Maladaptive stress responses occur when the body’s natural stress reactions become counterproductive, often due to factors such as chronic stress, unresolved trauma, or poor coping mechanisms. They become problematic when stress responses lead to persistent anxiety, and chronic health issues, or interfere with daily functioning and relationships. Signs include frequent emotional outbursts, persistent fatigue, or impaired social interactions. Strategies to manage and change maladaptive responses include developing healthier coping mechanisms, such as mindfulness and relaxation techniques, seeking professional support for underlying issues, and making lifestyle changes to reduce stressors and build resilience.
To manage stress responses effectively, practical tips include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Regular mindfulness practices and meditation help center your focus, reduce stress, and improve emotional regulation by fostering a calm state of mind.
- Therapy and Counseling: Seeking professional support from therapists can provide strategies for coping with stress, understanding underlying issues, and developing healthier responses.
- Physical Exercise: Regular physical activity helps release endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce stress levels.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, ensuring adequate sleep, and managing workload can support overall well-being and resilience.
Physiological and Emotional Regulation techniques include:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practicing deep, controlled breathing helps activate the parasympathetic nervous system, counteracting the stress response and promoting relaxation.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Systematically tensing and then relaxing muscle groups can reduce physical tension and stress.
- Cognitive Behavioral Techniques: Identifying and challenging negative thought patterns can help manage emotional responses and reframe stressors in a more manageable way.
Understanding stress responses like fight/flight and tend/befriend is essential for effective stress management. Fight/flight prepares you for immediate action but can lead to health issues if overused, while tend/befriend involves seeking support and nurturing relationships, which can be beneficial but may also lead to dependency if overdone. Maladaptive stress responses can interfere with daily life and health, so it’s important to adopt strategies like mindfulness, therapy, exercise, and healthy habits. Techniques such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation can help regulate stress.
Journaling Questions for Reflection:
- How do I typically react to stress: fight/flight, tend/befriend, or both?
- What signs indicate that my stress responses are becoming problematic?
- What stress management techniques work best for me, and how can I use them more often?
- Where in my life could I improve my stress responses or seek additional help?
- How can I incorporate mindfulness or relaxation techniques to better manage stress?